Precision Safety
Bearings are an indispensable part of modern medical devices, ensuring smooth and repeatable motion for diagnostic, therapeutic, and surgical platforms. From tomography imaging gantries to surgical robotic arms, infusion pumps, and dental handpieces, bearings convert motor torque into controlled motion. Their precision, friction characteristics, and durability directly affect image quality, surgical accuracy, patient safety, and equipment uptime.
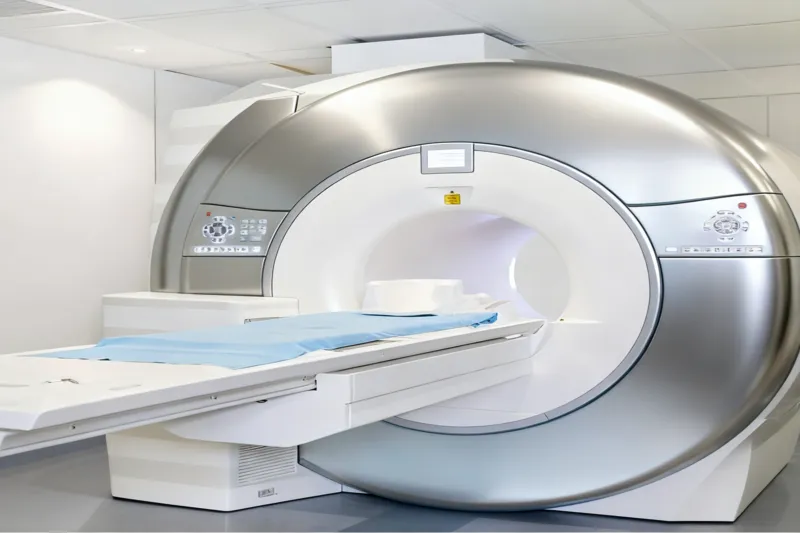
Imaging Systems—Low Vibration, High Speed
In CT, MRI, and X-ray equipment, bearings support rotating assemblies and gantry movements that must operate with extremely low vibration and minimal runout. High-precision deep groove ball bearings or cylindrical roller bearings with fine tolerances reduce micro-movements that cause image blurring. Low friction and thermal stability are crucial for limiting heat buildup and maintaining concentricity during extended scan cycles, thereby improving diagnostic resolution and patient throughput.
Surgical Robotics—Micro-Precision and Response Speed
Surgical robots require bearings capable of providing micron-level positioning accuracy and near-zero backlash. Crossed roller bearings, angular contact bearings, and custom miniature designs are commonly used in joint axes and instrument wrists. These bearings must combine high stiffness, predictable preload characteristics, and extremely low friction to enable fine force feedback and rapid, smooth motion—factors that critically impact surgical outcomes.
Therapeutic and Life Support Equipment
Components in dialysis machines, infusion pumps, ventilators, and prosthetic drivers require optimized bearings for continuous operation and low maintenance. Sealed bearings with biocompatible lubricants or solid lubrication alternatives (PTFE, DLC coatings) prevent contamination and meet extended maintenance intervals. Selected materials and lubricants can withstand daily cleaning, disinfection, and occasional sterilization cycles without performance degradation.
Sterilization and Biocompatibility—Material Selection
Medical environments have stringent hygiene standards. Bearings for reusable instruments or autoclavable modules are manufactured from corrosion-resistant stainless steel, ceramics, or coated alloys. Designs must withstand steam sterilization, gamma radiation, or chemical sterilization; seal and cage materials are chosen to maintain integrity and prevent particle generation that could compromise sterile areas or imaging systems.
Electrical and Magnetic Field Considerations—Noise and Interference
In electrically sensitive equipment (such as imaging consoles, MRI gradient drivers, and actuators), bearing materials and grounding strategies must minimize electrostatic discharge and electromagnetic interference (EMI). The use of non-conductive ceramic balls in bearings or properly grounded conductive paths can reduce the risk of pitting caused by stray currents and help extend bearing life in electrically active environments.
Testing and Regulatory Compliance—Verified Performance
Medical bearings undergo rigorous testing: endurance tests, particulate emission tests, biocompatibility assessments, and sterilization cycle validations. Traceable quality systems and material certifications support device approvals and ensure reliable performance throughout the clinical lifecycle.
Empowering Medical Devices to Enhance Service Quality
In medical devices, bearings are far more than mechanical supports; they are key to precise diagnosis and treatment. Carefully selected bearings—balancing precision, biocompatibility, disinfection resistance, and lifespan reliability—can directly improve patient outcomes, reduce downtime, and elevate the performance of modern medical technologies.
● Bearing Types: High-precision cylindrical roller bearings and ball bearings. Miniature precision bearings